Confidence Intervals – CASP
The p-value gives no direct indication of how large or important the estimated effect size is. So, confidence intervals are often preferred.
| 0 Comments | Evaluated
Know Your Chances
This book has been shown in two randomized trials to improve peoples' understanding of risk in the context of health care choices.
| 0 Comments | Evaluated
Association is not the same as causation. Let’s say that again: association is not the same as causation!
This article explains how to tell when correlation or association has been confused with causation.
| 0 Comments
Calling Bullshit Syllabus
Carl Bergstrom's and Jevin West's nice syllabus for 'Calling Bullshit'.
| 0 Comments
‘Tricks to help you get the result you want from your study (S4BE)
Inspired by a chapter in Ben Goldacre’s ‘Bad Science’, medical student Sam Marks shows you how to fiddle research results.
| 0 Comments
It’s just a phase
A resource explaining the differences between different trial phases.
| 0 Comments
Strictly Cochrane: a quickstep around research and systematic reviews
An interactive resource explaining how systematic and non-systematic reviews differ, and the importance of keeping reviews up to date.
| 0 Comments
The Princess and the p-value
An interactive resource introducing reporting and interpretation of statistics in controlled trials.
| 0 Comments

Teach Yourself Cochrane
Tells the story behind Cochrane and the challenges finding good quality evidence to produce reliable systematic reviews.
| 3 Comments
Fast Stats to explain absolute risk, relative risk and Number Needed to Treat (NNT).
A 15-slide presentation on ‘Fast Stats’ to explain absolute risk, relative risk and Number Needed to Treat (NNT) prepared by PharmedOut.
| 0 Comments
Critical appraisal
University of New South Wales Medical Statistics Tutorial 4 addresses Critical Appraisal.
| 0 Comments
Probability and tests of statistical significance
University of New South Wales Medical Statistics Tutorial 6 addresses ‘Probability and tests of statistical significance’.
| 0 Comments
Bias – the biggest enemy
University of New South Wales Medical Stats Online Tutorial 5 addresses ‘Bias - the biggest enemy’.
| 0 Comments
Introduction to Evidence-Based Medicine
Bill Caley’s 26 slides with notes used as an ‘Introduction to Evidence-Based Medicine’.
| 0 Comments
Applying evidence to patients
A 27-minute talk on ‘Applying Evidence to Patients’, illustrated by 17 slides, with notes.
| 0 Comments
2×2 tables and relative risk
A 10-min talk on ‘2x2 tables and Relative Risk’, illustrated by 14 slides, with notes.
| 0 Comments
Appraisal of evidence and interpretation of results
A 14-min talk on ‘Appraisal of the Evidence and Interpretation of the Results’, illustrated by 19 slides, with notes.
| 0 Comments
Basic principles of randomised trials, and validity
A 8-min talk on ‘Basic principles of Randomised Trials, and Validity’, illustrated by 15 slides, with notes.
| 0 Comments
Defining clinical questions
An 8-min talk on ‘Defining Clinical Questions’ illustrated by 10 slides, with notes.
| 0 Comments
A way to teach about systematic reviews
81 slides used by David Nunan (Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford) to present ‘A way to teach about systematic reviews’.
| 0 Comments
Applying the evidence
Six key slides produced by the University of Western Australia on applying evidence in practice.
| 0 Comments
Applying the results of trials and systematic reviews to individual patients
Paul Glasziou uses 28 slides to address ‘Applying the results of trials and systematic reviews to individual patients’.
| 0 Comments
10 Components of effective clinical epidemiology: How to get started
PDF & Podcast of 1-hr talk by Carl Heneghan (Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford) on effective clinical epidemiology.
| 0 Comments
Critical appraisal of clinical trials
Slides developed by Amanda Burls for an interactive presentation covering the most important features of well controlled trials.
| 0 Comments
Applying Systematic Reviews
How useful are the results of trials in a systematic review when it comes to weighing up treatment choices for particular patients?
| 0 Comments
Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis: Information Overload
None of us can keep up with the sheer volume of material published in medical journals each week.
| 0 Comments
Combining the Results from Clinical Trials
Chris Cates notes that emphasizing the results of patients in particular sub-groups in a trial can be misleading.
| 0 Comments
GenerationR – The importance of involving children and young people in research
3/3, 22-min video at the launch of GenerationR, a network of young people who advise researchers.
| 0 Comments
Generation R – The importance of medical research in children and young people
2/3, 35-min video at the launch of GenerationR, a network of young people who advise researchers.
| 0 Comments
Generation R – The need to reduce waste in clinical research involving children
1/3, 14-min video at the launch of GenerationR, a network of young people who advise researchers.
| 0 Comments
No Power, No Evidence!
This blog explains that studies need sufficient statistical power to detect a difference between groups being compared.
| 0 Comments
Beginners guide to interpreting odds ratios, confidence intervals and p values
A tutorial on interpreting odds ratios, confidence intervals and p-values, with questions to test the reader’s knowledge of each concept.
| 0 Comments
Sample Size matters even more than you think
This blog explains why adequate sample sizes are important, and discusses research showing that sample size may affect effect size.
| 0 Comments
What is it with Odds and Risk?
This blog explains odds ratios and relative risks, and provides the formulae for calculating both measures.
| 0 Comments
Preclinical animal studies: bad experiments cost lives
This blog notes that few therapies that treat disease in animals successfully translate into effective treatments for humans.
| 0 Comments
Surrogate Endpoints in EBM: What are the benefits and dangers?
What are surrogate outcomes, their pros and cons, and why you should be cautious in extrapolating from them to clinical decisions.
| 0 Comments
The Systematic Review
This blog explains what a systematic review is, the steps involved in carrying one out, and how the review should be structured.
| 0 Comments
The Mean: Simply Average?
This blog explains ‘the mean’ as a measure of average; describes how to calculate it; and flags up some caveats.
| 0 Comments
Publication Bias: An Editorial Problem?
A blog challenging the idea that publication bias mainly occurs at editorial level, after research has been submitted for publication.
| 0 Comments
The Bias of Language
Publication of research findings in a particular language may be prompted by the nature and direction of the results.
| 0 Comments
Defining Bias
This blog explains what is meant by ‘bias’ in research, focusing particularly on attrition bias and detection bias.
| 0 Comments
Balancing Benefits and harms
A blog explaining what is meant by ‘benefits’ and ‘harms’ in the context of healthcare interventions, and the importance of balancing them.
| 0 Comments
Data Analysis Methods
A discussion of 2 approaches to data analysis in trials - ‘As Treated’, and ‘Intention-to-Treat’ - and some of the pros and cons of each.
| 0 Comments
Defining Risk
This blog defines ‘risk’ in relation to health, and discusses some the difficulties in applying estimates of risk to a given individual.
| 0 Comments
Traditional Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
This blog outlines 11 differences between systematic and traditional reviews, and why systematic reviews are preferable.
| 0 Comments
P Value in Plain English
Using simple terms and examples, this blog explains what p-values mean in the context of testing hypotheses in research.
| 0 Comments
Cancer Screening Debate
This blog discusses problems that can be associated with cancer screening, including over-diagnosis and thus (unnecessary) over-treatment.
| 0 Comments
Surrogate endpoints: pitfalls of easier questions
A blog explaining what surrogate endpoints are and why they should be interpreted cautiously.
| 0 Comments
Misconceptions about screening
Screening should not be for everyone or all diseases. It should only be offered when it is likely to do good than harm.
| 0 Comments
Making sense of randomized trials
A description of how clinical trials are constructed and analysed to ensure they provide fair comparisons of treatments.
| 0 Comments
Randomized Control Trials
1/2, 40-min lecture on randomized trials by Dr R Ramakrishnan (Lecture 25) for the Central Coordinated Bioethics Programme in India.
| 0 Comments
Compliance with protocol and follow-up in clinical trials
Denis Black’s 10-min, downloadable, PowerPoint presentation on compliance, follow up, and intention-to-treat analysis in clinical trials.
| 0 Comments
Clinical Significance – CASP
To understand results of a trial it is important to understand the question it was asking.
| 0 Comments
Statistical Significance – CASP
In a well-conducted randomized trial, the groups being compared should differ from each other only by chance and by the treatment received.
| 0 Comments
Making sense of results – CASP
This module introduces the key concepts required to make sense of statistical information presented in research papers.
| 0 Comments
Screening – CASP
This module on screening has been designed to help people evaluate screening programmes.
| 0 Comments

Randomised Control Trials – CASP
This module looks at the critical appraisal of randomised trials.
| 0 Comments
Tamiflu: securing access to medical research data
A campaign by researchers has shown that Roche spun the research on Tamiflu to meet their commercial ends.
| 0 Comments
Los intervalos de confianza en investigación
¿Para qué sirven los intervalos de confianza en los estudios de investigación?
| 0 Comments

Watson en busca de la evidencia
Cómic acerca de conflictos de intereses y búsqueda de información.
| 0 Comments
Why avoiding differences between treatments allocated and treatments received is important
Knowledge of which treatments have been received by which study participants can affect adherence to assigned treatments and result in bias.
| 0 Comments
The need to avoid differences in the way treatment outcomes are assessed
Biased treatment outcome assessment can result if people know which participants have received which treatments.
| 0 Comments
Using the results of up-to-date systematic reviews of research
Trustworthy evidence from research is necessary, but not sufficient, to improve the quality of health care.
| 0 Comments
Introduction to JLL Explanatory Essays
Professionals sometimes harm patients by using inadequately evaluated treatments. Research addressing uncertainties can reduce this harm.
| 0 Comments
Avoiding biased treatment comparisons
Biases in tests of treatments are those factors that can lead to conclusions that are systematically different from the truth.
| 0 Comments
Recognizing researcher/sponsor biases and fraud
The vested interests of researchers and organizations tend to be reflected in reports of treatment research in which they are involved.
| 0 Comments
Interpreting 95% Confidence Intervals
Gilbert Welch’s 9-min video on how 95% confidence intervals relate to p values.
| 0 Comments
What are systematic reviews?
A 3-min video by Jack Nunn and The Cochrane Consumers and Communication group for people unfamiliar with the concept of systematic reviews.
| 0 Comments
Interactive PowerPoint Presentation about Clinical Trials
An interactive Powerpoint presentation for people thinking about participating in a clinical trial or interested in learning about them.
| 0 Comments

Introduction to clinical trials: lay-friendly video
This lay-friendly video introduction to clinical trials was created by the European Communication on Research Awareness Needs Project.
| 3 Comments
Overview of study designs
11 slides and a 4-min commentary overviewing study designs for clinical research. (from Univ Mass Med School).
| 1 Comment
Systematic Reviews
3 slides and a 4-min commentary about systematic reviews and meta-analyses (from Univ Mass Med School).
| 0 Comments
Relative risk, absolute risk and number-needed-to-treat
8 slides and a 4-min commentary on relative risk, absolute risk, and number needed to treat (from Univ Mass Med School).
| 0 Comments
Attrition bias, publication bias, comparator bias and commercial bias
6 slides and a 3-min commentary on attrition bias, publication bias, comparator bias and commercial bias (from Univ Mass Med School).
| 0 Comments
P-values and the role of chance
Gilbert Welch’s 10-min video on p-values and assessing the likelihood that a difference between treatments is due to chance.
| 0 Comments
Understanding Confidence Intervals
A 4-min video explaining the concept of confidence intervals and how they are calculated, with helpful diagrams and examples.
| 0 Comments
Understanding Overdiagnosis bias
Gilbert Welch’s 14-min video discussing the risks of overdiagnosis bias and screening.
| 0 Comments
Calculating and interpreting absolute and relative change in an unwanted outcome after treatment
Gilbert Welch’s 6-min video explaining how to calculate and interpret absolute and relative change in an unwanted outcome.
| 0 Comments
Understanding lead-time bias
Gilbert Welch’s 10-min video explaining why survival ALWAYS rises following early detection -- even if no one is helped.
| 0 Comments
Testing Treatments Audio Book
The Testing Treatments Audiobook enables visitors to the TTi site to select whichever chapters in the book they would like to listen to.
| 0 Comments
Double blind studies
A webpage discussing the importance of blinding trial participants and researchers to intervention allocation.
| 0 Comments
CEBM – Study Designs
A short article explaining the relative strengths and weaknesses of different types of study design for assessing treatment effects.
| 0 Comments
Introduction to Critical Appraisal
30-slide introduction by Jason Curtis, to Critical Appraisal.
| 0 Comments
DISCERN online
A questionnaire providing a valid and reliable way of assessing the quality of written information on treatment choices.
| 0 Comments
Means vs. Medians
Keith Bower’s 3-min video explaining how means (averages) and medians can be presented misleadingly.
| 0 Comments
Randomized Controlled Trial Protocols
A 1-hour videoed lecture explaining protocols for Randomized Control Trials (RCTs).
| 0 Comments
John Ioannidis, the scourge of sloppy science
A 8 min podcast interview with John Ioannidis explaining how research claims can be misleading.
| 0 Comments
Science Weekly Podcast – Ben Goldacre
A 1-hour audio interview with Ben Goldacre discussing misleading claims about research.
| 0 Comments
Statistical Significance and Practical Significance
Keith Bower’s 3-min video discussing the difference between Statistical Significance and Practical Significance.
| 0 Comments
Signals of overdiagnosis
Gilbert Welch’s 8-min video showing how population screening for disease leads to overdiagnosis.
| 0 Comments
Randomised Controlled Trials vs. Observational Studies
5-minute video explaining the difference between randomised trials and observational studies.
| 0 Comments
Type I and Type II errors, and how statistical tests can be misleading
Gilbert Welch’s 12-min video explaining Type I and Type II errors, and how statistical tests can be misleading.
| 0 Comments
How do you know which healthcare research you can trust?
A detailed guide to study design, with learning objectives, explaining some sources of bias in health studies.
| 0 Comments
Smart Health Choices: making sense of health advice
The Smart Health Choices e-book explains how to make informed health decisions.
| 0 Comments
Methodology of clinical trials
Eurordis training on the methodology of clinical trials for representatives of patients’ organisations.
| 0 Comments
Can measurements show if a treatment works?
An article discussing errors to avoid when testing treatments.
| 0 Comments
More than average confusion about what mean means mean
Cartoon and blog about how averages can hide important variations in effects.
| 0 Comments
In defence of systematic reviews of small trials
An article discussing the strengths and weaknesses of systematic reviews of small trials.
| 0 Comments
Mega-trials
In this 5 min audio resource, Neeraj Bhala discusses systematic reviews and the impact of mega-trials.
| 0 Comments
Relative or absolute measures of effects
Dr Chris Cates' article explaining absolute and relative effects of treatment effects.
| 0 Comments
Evidence from Randomised Trials and Systematic Reviews
Dr Chris Cates' article discussing control of bias in randomised trials and explaining systematic reviews.
| 0 Comments
The perils and pitfalls of subgroup analysis
Dr Chris Cates' article demonstrating why subgroup analysis can be untrustworthy.
| 0 Comments
Reporting results of studies
Dr Chris Cates' article discussing how to report study results, with emphasis on P-values and confidence intervals.
| 0 Comments
Disease outcomes vs. patient-relevant outcomes
An e-Learning module consisting of 3 slides and 2-min commentary on why it is important to treat patients, not numbers from tests.
| 0 Comments
Routine use of unvalidated therapy is less defensible than careful research to assess the effects of those treatments
It is more difficult to obtain consent to give a treatment in a clinical trial than to give the same treatment for patients in practice.
| 2 Comments
Viva la Evidence!
A brilliant song and video by James McCormack explaining the basics of evidence-based medicine.
| 0 Comments
Evidence Based Medicine Matters: Examples of where EBM has benefitted patients
Booklet containing 15 examples submitted by Royal Colleges where Evidence-Based Medicine has benefited clinical practice.
| 0 Comments
Big data and finding the evidence
“Big data” is large-scale data processing technologies intended to generate insights into performance, behaviour and trends.
| 0 Comments
Some Studies That I Like to Quote
This short music video encourages health professionals to use evidence to help reach treatment decisions in partnership with patients.
| 0 Comments
What does the Cochrane logo tell us?
This video and animated slide presentation prepared by Steven Woloshin shows how the Cochrane logo was developed, and what it tells us.
| 3 Comments
On taking a good look at ourselves
Iain Chalmers talks about failings in scientific research that lead to avoidable harm to patients and waste of resources.
| 1 Comment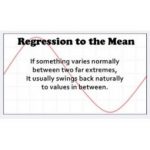
A poem about regression to the mean
Regression to the mean can lead us to think that an intervention has been effective when it hasn't. This poem illustrates it nicely.
| 0 Comments
What does a positive genetic test mean? The example of coeliac disease
Video tutorial explores the ways in which evidence about the effectiveness of genetic testing can be misrepresented in advertising.
| 0 Comments
บทที่ 1 ใหม่กว่าแล้วดีกว่าไหม
ประเด็นสำคัญ การตรวจสอบวิธีเป็นเรื่องจำเป็น เพราะวิธีการรักษาใหม่มีโอกาสพอๆ กันที่จะแย่กว่า หรือดีกว่าวิธีการรักษาที่ใช้กันอยู่ การตรวจสอบวิธีการรักษาที่ (ไม่เที่ยงธรรม) อาจทำให้ผู้ป่วยทุกข์ทรมานและเสียชีวิต วิธีการรักษาที่อนุมัติให้ใช้แล้วก็ใช่ว่าปลอดภัยเสมอไป ต้องใช้เวลาระยะหนึ่งกว่าอาการข้างเคียงจากวิธีการรักษาจะปรากฏ จากวิธีการรักษามักถูกเน้นเกินจริง ขณะที่มักถูกกลบเกลื่อน ทำไมต้องมีการตรวจสอบวิธีการรักษาอย่างเที่ยงธรรม หากขาดการประเมินอย่างเที่ยงธรรม…คือไม่ลำเอียง…ก็อาจมีการสั่งใช้วิธีการรักษาที่ไม่ได้ผลหรือกระทั่งเป็นโทษเพราะนึกว่ามีประโยชน์ หรือตรงข้าม การรักษาที่ได้ผลก็อาจถูกละเลยเพราะมองว่าไม่มีประโยชน์ จึงควรตรวจสอบอย่างเที่ยงธรรมกับวิธีการรักษาทุกวิธี โดยไม่ต้องสนใจว่ามันมีที่มาอย่างไร หรือเป็นวิธีมาตรฐานหรือวิธีเสริม/ทางเลือกหรือไม่ ไม่ควรเชื่อทฤษฎีเกี่ยวกับผลของวิธีการรักษาที่ยังไม่ได้ตรวจสอบ […]
| 0 CommentsNo Resources Found
Try clearing your filters or selecting different ones.
